-
MYP
- Home
-
IGCSE
- Course information
-
Physical: Hazardous environments
>
- Distribution of tectonic hazards
- Causes of tsunami
- Measuring earthquakes
- Earthquake case study 1: Haiti
- Earthquake case study 2: Christchurch
- Why do earthquakes do more damage in LICs than in HICs?
- How are volcanic eruptions measured?
- Tropical storms - distribution
- Causes of tropical cyclones
- Tropical cyclones - case study
- Why live in hazardous areas?
-
River Environments
>
- Hydrological cycle
- River basins
- Factors affecting river regimes
- Fluvial processes: erosion
- Fluvial processes: weathering and mass movement
- Fluvial processes: transportation and depositon
- River features and their formation
- How rivers change from source to mouth
- Uses of water
- Water pollution
- Water supply
-
IBDP
-
Changing population
>
- Global patterns of economic development
- Physical and human factors affecting global population distribution
- Case study 1: China
- Case study 2: Niger
- Demographic transition
- Megacity growth
- Forced migration and internal displacement
- Ageing populations
- Pro-natalist and anti-natalist policies
- Gender equality policies
- Trafficking policies
- The Demographic Dividend
-
Global climate vulnerability and resilience
>
- Atmospheric system
- The energy balance
- Changes in the energy balance
- The enhanced greenhouse effect
- Climate Change and the Hydrosphere, Atmosphere and Biosphere
- Impacts of climate change on people and places
- Disparities in exposure to climate change risk and vulnerability
- Government-led adaptation and mitigation strategies
- Civil society and corporate strategies
-
Global resource consumption and security
>
- Progress towards poverty reduction
- Measuring trends in global consumption
- Global patterns and trends in the availability and consumption of water
- Global patterns and trends in the availability and consumption of land/food
- Global patterns and trends in the availability and consumption of energy
- Water food and energy nexus
- Recycling and waste
- Malthus vs Boserup
- Resource Stewardship strategies
- Sustainable Development Goals
-
Freshwater - drainage basins
>
- The drainage basin as a system
- How rivers change from source to mouth
- River discharge
- River processes
- River landforms
- Factors affecting flood risk
- Attempts at flood prediction
- Flood mitigation
- Flood mitigation case studies
- Water scarcity
- Agricultural activities and water quality
- Pressures on lakes and aquifers
- Internationally shared water and conflict
- Water management: participation of local communities
- Dams as multi-purpose schemes
- Water management: Integrated Drainage Basin Management (IDBM)
- Managing wetlands
-
Leisure, Sport and Tourism
>
- Growth and purpose of leisure time
- Categories of tourism and sport
- Economic development and participation
- Factors affecting personal participation
- Factors affecting growth of tourism hotspots
- Spheres of influencee
- Factors affecting a national sports league
- Festivals
- Niche national tourism strategies
- Role of TNCs
- Tourism as a national development strategy
- International sporting events
- Consequences of unsustainable growth
- Sustainable tourism
- Future international tourism
- Political and cultural influences on sport
- Extended Essay in Geography >
- Skills/concepts >
-
Changing population
>
- Geography and ToK
- Theory of Knowledge
Study Guide
The link between economic development and participation in leisure activities
• Detailed examples to illustrate recent changes in participation for two or more societies at contrasting stages of development
• Detailed examples to illustrate recent changes in participation for two or more societies at contrasting stages of development
Why would we expect a link between economic development and participation in leisure activities?
1. Greater wealth = more leisure time?
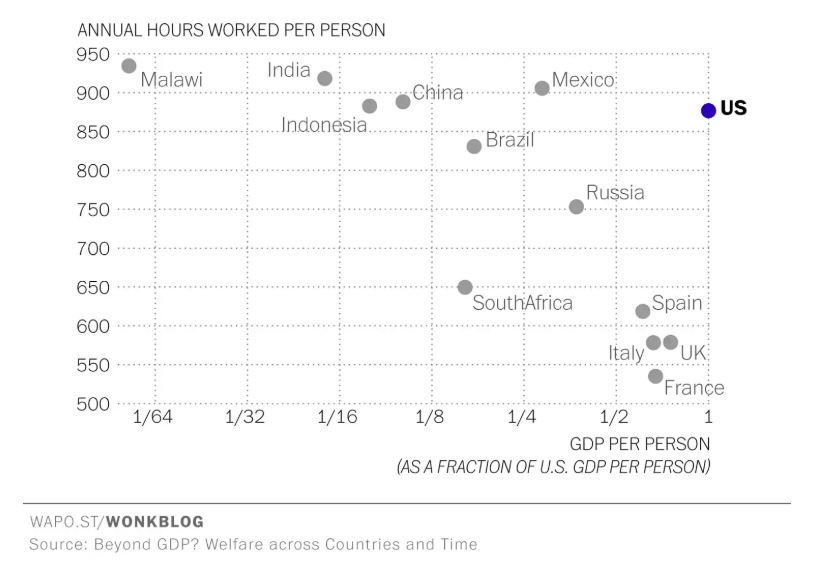
Study the graph below from the Washington Post.
|
|
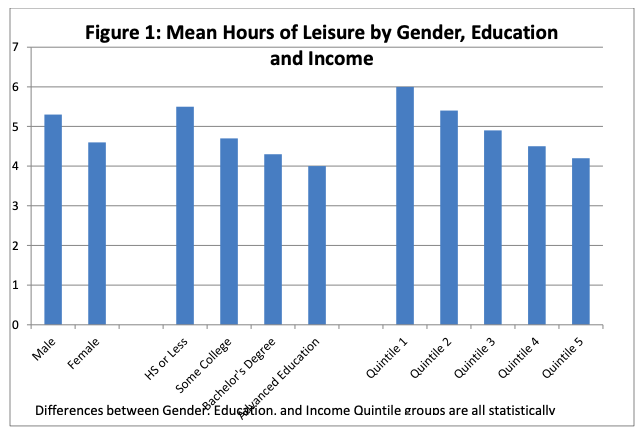
The graph, right, shows average hours of leisure time in the US by gender, education and income. Describe the patterns shown. What do they say about economic development/wealth and likely participation in leisure activities? |
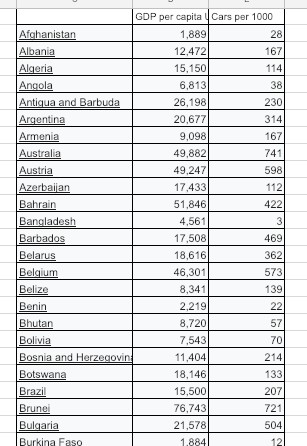
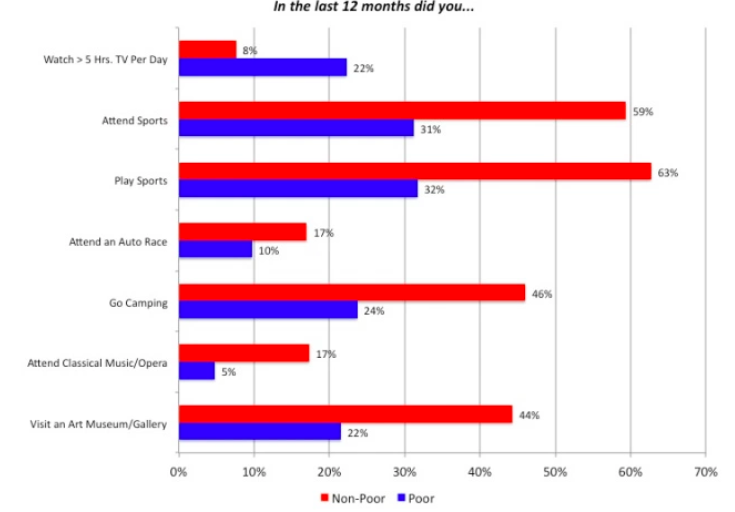
2. Personal and national income affects access and choice in leisure activities
|
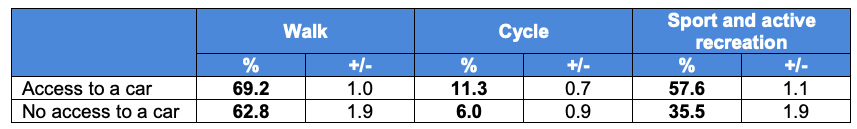
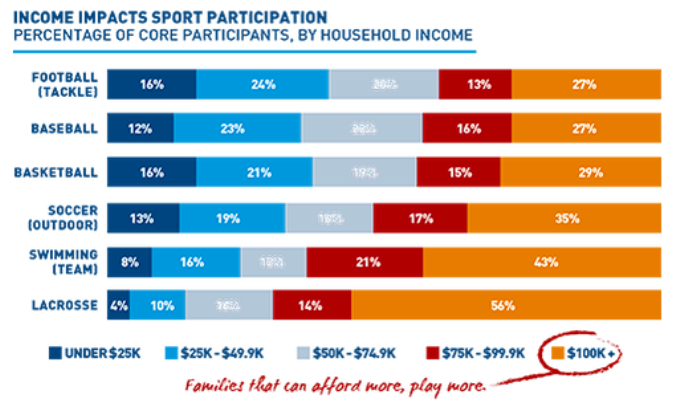
4. Examine the leisure activities below. In pairs, choose four and explain how people's likelihood of participating will be influenced by the level of economic development of their home country and by personal wealth.
|
The graph on the left is based upon questions about leisure activities asked of adult respondents to the United States general social survey (GSS) since the 1990s.
|
3. Other socio-economic factors
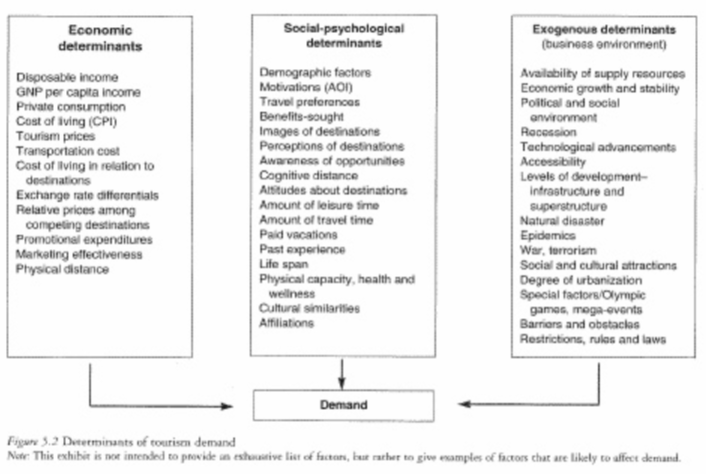
The diagram below shows some suggested factors affecting demand for tourism. Examine them carefully and establish which you believe are:
- Directly caused by the level of economic development of a country or region.
- Indirectly caused by level of economic development.
- Connected to personal wealth and status.
- Unconnected to economic factors.
Example 1: Tourism growth and development in China
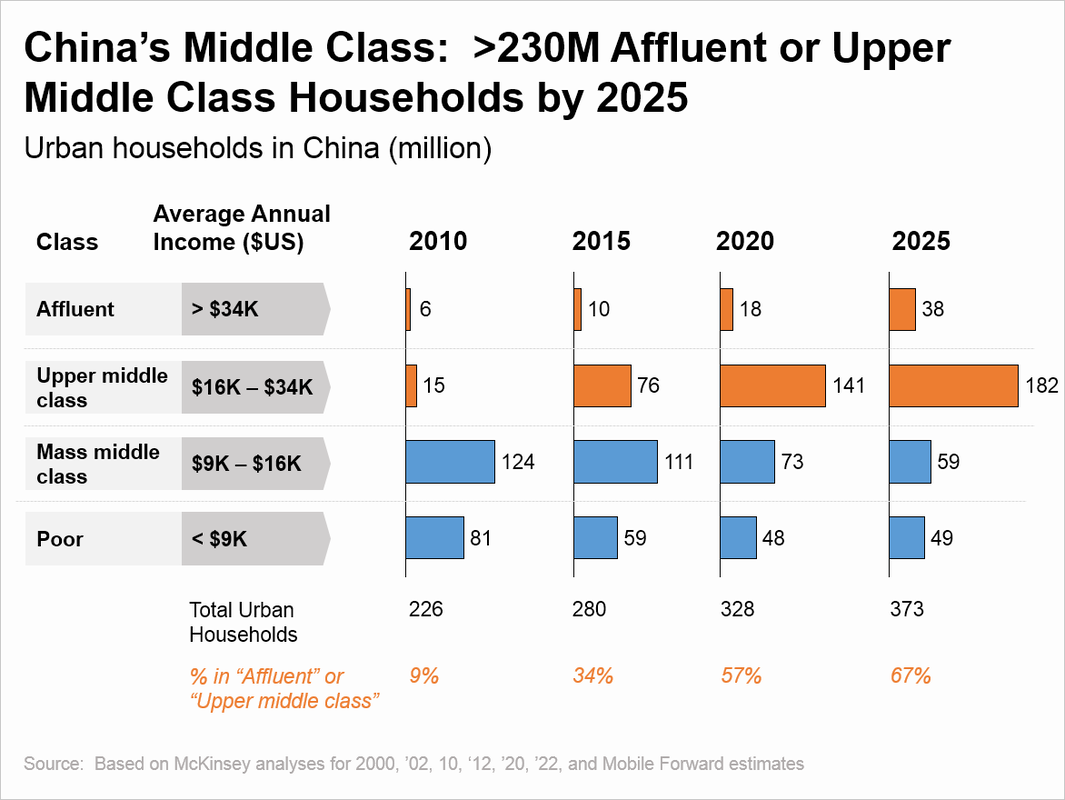
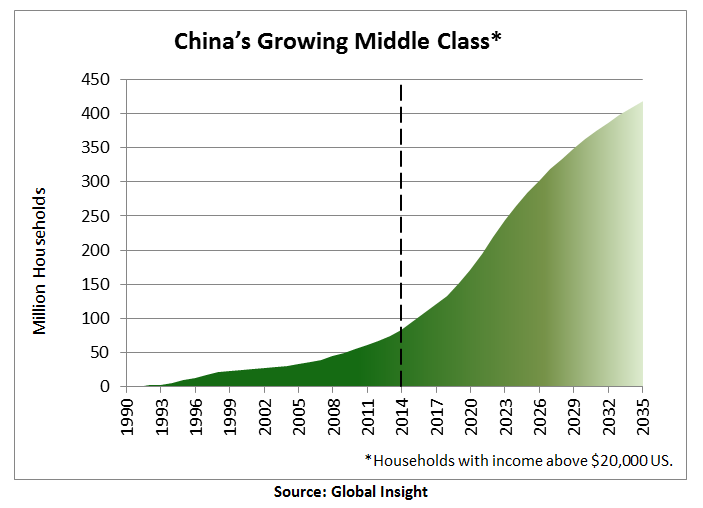
Study the resources below which show the rise of the middle class in China. First, make sure you remember the work we have already done on the emergence of the global middle class.
- Study the graph on the left and identify the most significant changes shown. Use data to describe the changes.
- Now study the graph on the right. Again describe the pattern of change using data to support your answer.
- What can we infer from this data on the amount of disposable income available to these middle class and especially upper middle class people?
- How would we expect this to affect their participation in leisure and tourism activities?
Next watch the video clip below. Identify:
- Three key points
- Two important statistics on leisure participation amongst Chinese people
- One interesting fact or aspect of the story
Now examine the resources below.
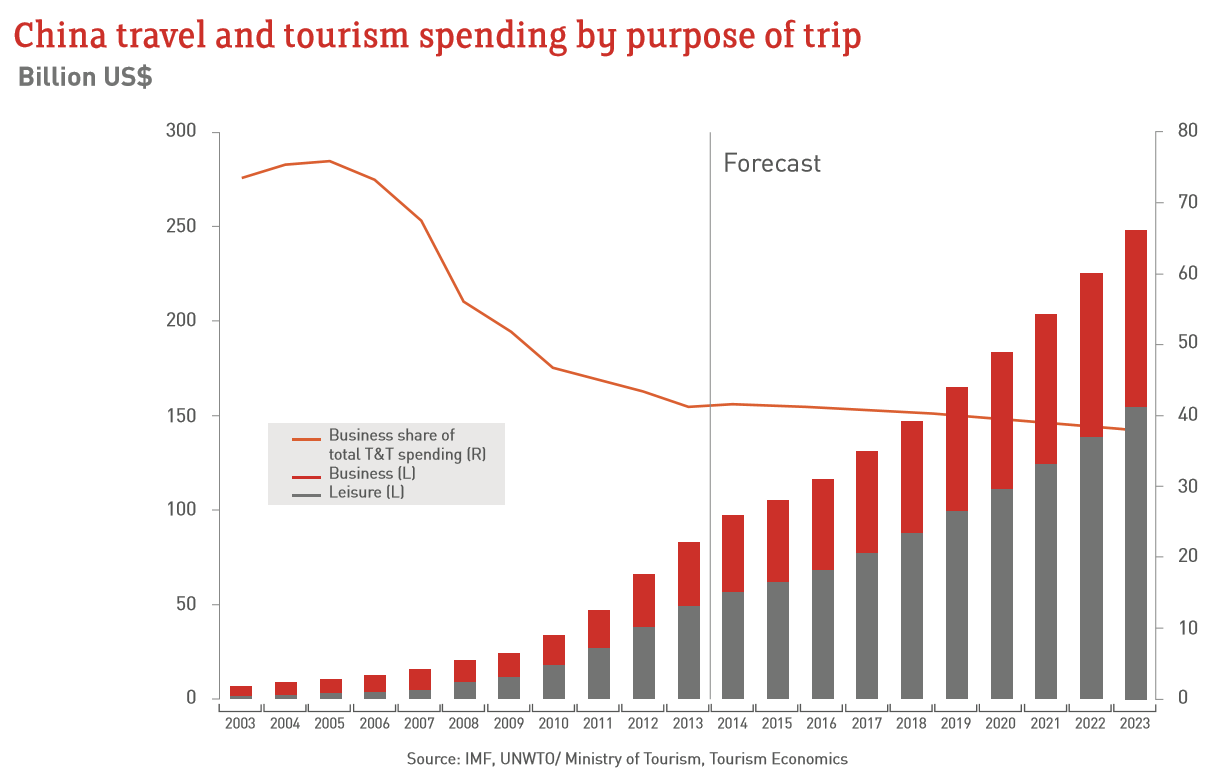
- Start with the graph on the left. What does the line graph show? What pattern is shown? Try to explain why.
- Now study the stacked bar graphs. What patterns are shown? Explain the change in both business and leisure trips.
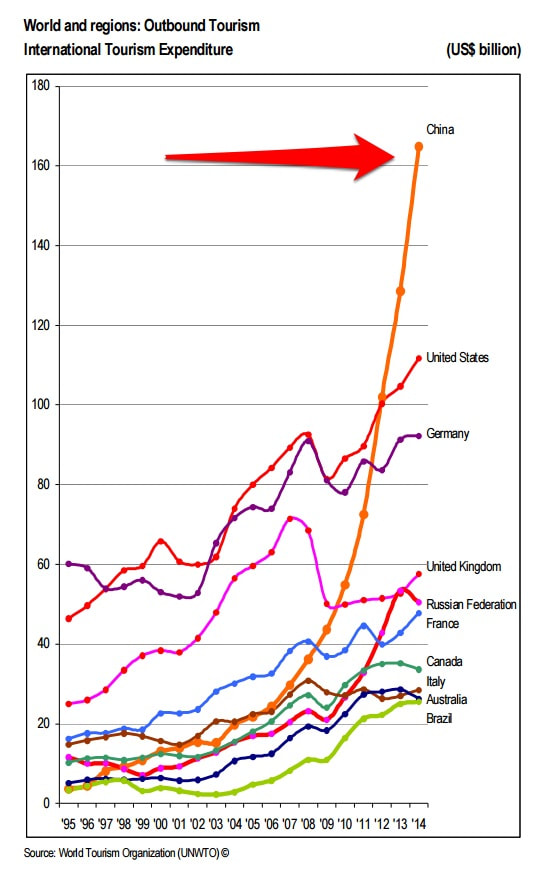
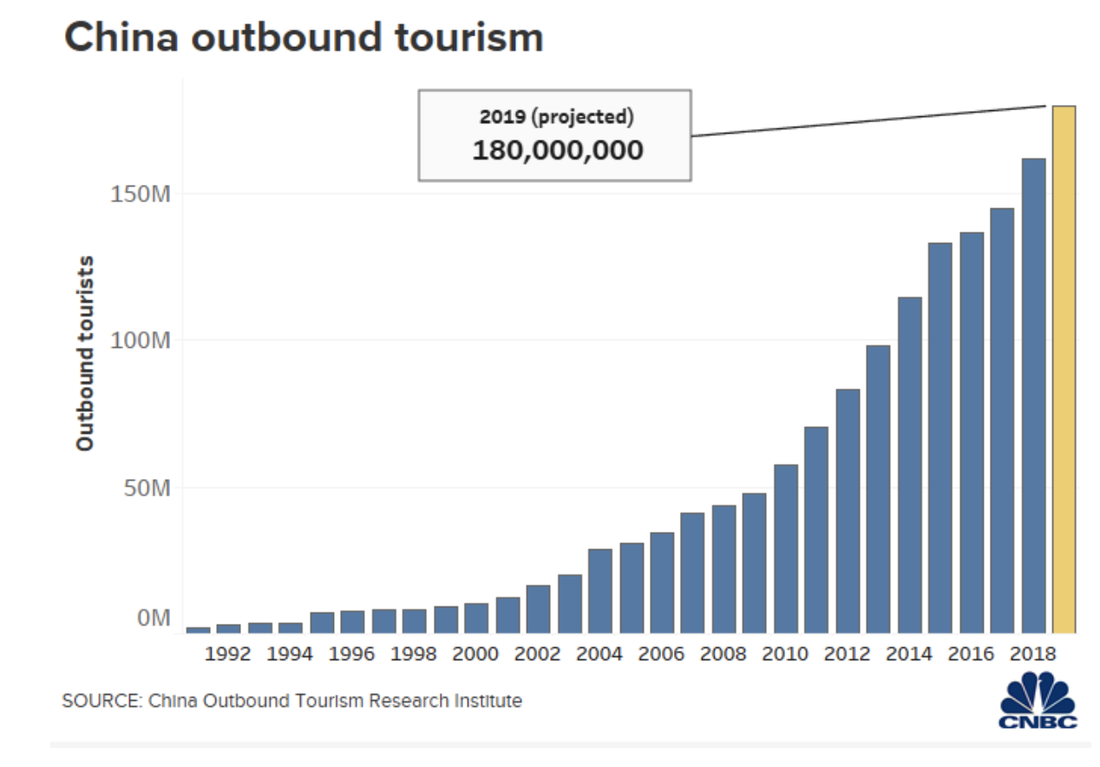
- From the graph on the right, describe the pattern of growth in outbound tourism from China between 1996 and 2014. Use data to compare the rate of growth in outbound tourism from China with the other countries shown. Explain the patterns.
- Now read the two articles (the images are hyperlinked). Use these to add depth and detail to your explanation of the patterns shown and the reason for the huge increase in tourism in China.
Finally, consider some of the positive and negative consequences of the huge growth in Chinese tourism. Examine the resources below and create a simple SWOT analysis of the impacts that this changes in participation in leisure has had in and out of China.
Example 2: Female golfers in South Korea
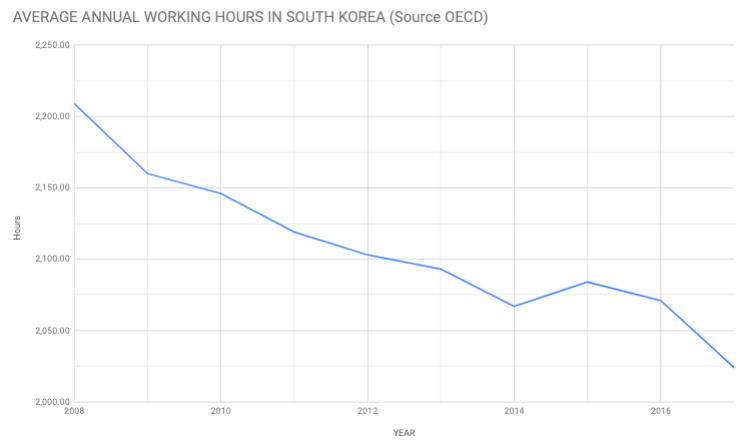
Study the two graphs below:
- Describe with data the changes in GDP per capita in South Korea from 1910 to the present. What can we infer from this about personal income and availability of leisure choices?
- The second graph shows changes in the the average number of annual working hours in South Korea. Working hours in South Korea are high compared to most OECD countries but area falling rapidly.
- Describe how working hours in South Korea have changed since 2009. What implications does this have for leisure time in the country?
|
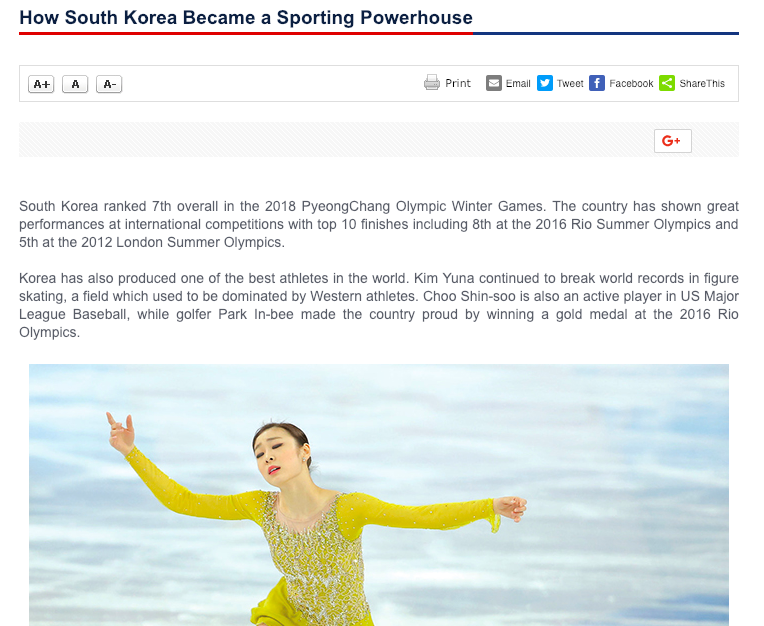
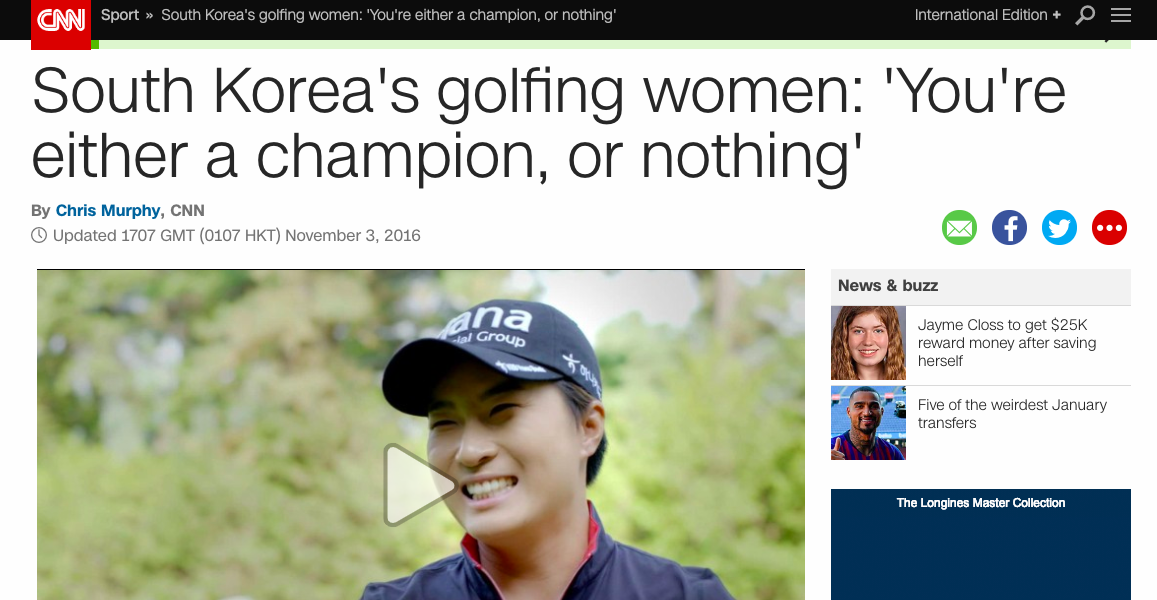
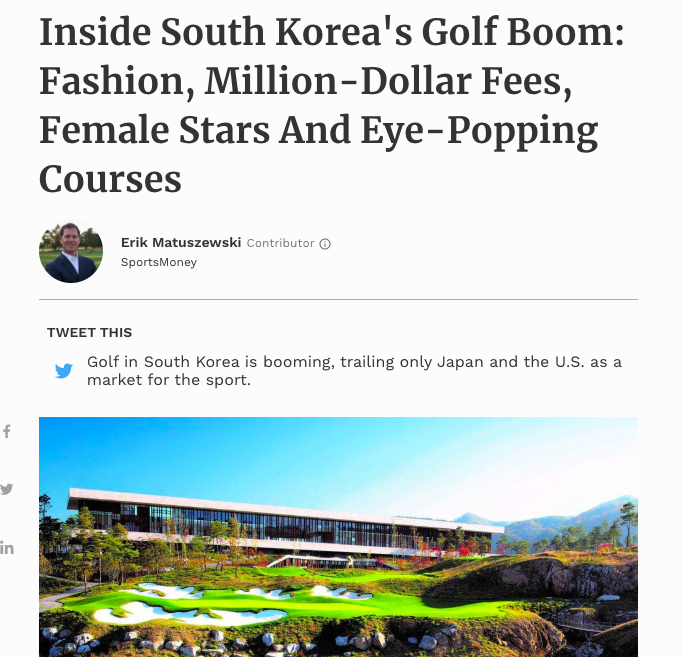
Read the article of the right and identify the role played by each of the following in developing South Korea as a sporting nation:
|
Watch the video and examine the website below. What factors do you think have led to the growth of golfing in South Korea and to the success of Korean players? Consider:
- investment
- quality of courses
- growth of a golfing culture
- culture and attitudes to golf
- media presentation
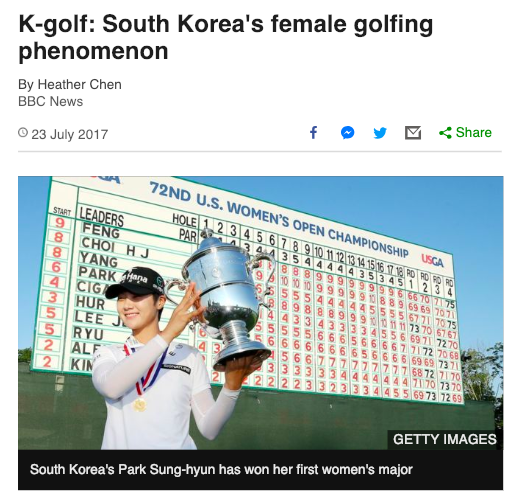
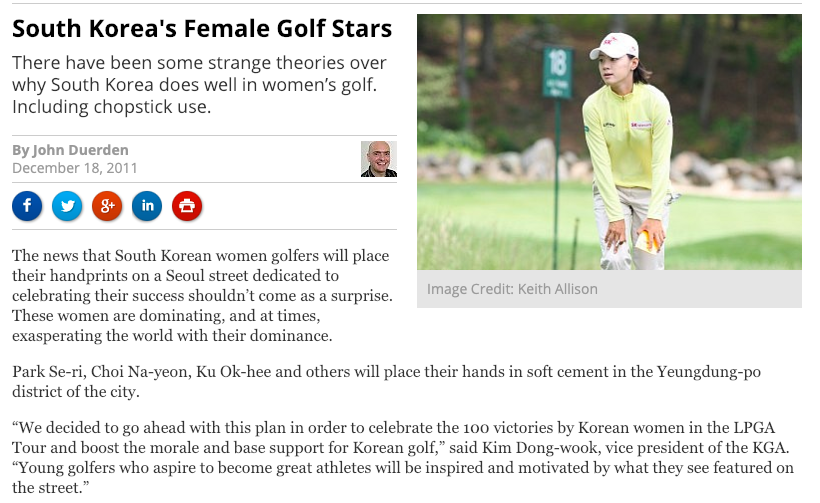
Finally, examine the resources below and identify the factors which have made golf so attractive to South Korean women.