-
MYP
- Home
-
IGCSE
- Course information
-
Physical: Hazardous environments
>
- Distribution of tectonic hazards
- Causes of tsunami
- Measuring earthquakes
- Earthquake case study 1: Haiti
- Earthquake case study 2: Christchurch
- Why do earthquakes do more damage in LICs than in HICs?
- How are volcanic eruptions measured?
- Tropical storms - distribution
- Causes of tropical cyclones
- Tropical cyclones - case study
- Why live in hazardous areas?
-
River Environments
>
- Hydrological cycle
- River basins
- Factors affecting river regimes
- Fluvial processes: erosion
- Fluvial processes: weathering and mass movement
- Fluvial processes: transportation and depositon
- River features and their formation
- How rivers change from source to mouth
- Uses of water
- Water pollution
- Water supply
-
IBDP
-
Changing population
>
- Global patterns of economic development
- Physical and human factors affecting global population distribution
- Case study 1: China
- Case study 2: Niger
- Demographic transition
- Megacity growth
- Forced migration and internal displacement
- Ageing populations
- Pro-natalist and anti-natalist policies
- Gender equality policies
- Trafficking policies
- The Demographic Dividend
-
Global climate vulnerability and resilience
>
- Atmospheric system
- The energy balance
- Changes in the energy balance
- The enhanced greenhouse effect
- Climate Change and the Hydrosphere, Atmosphere and Biosphere
- Impacts of climate change on people and places
- Disparities in exposure to climate change risk and vulnerability
- Government-led adaptation and mitigation strategies
- Civil society and corporate strategies
-
Global resource consumption and security
>
- Progress towards poverty reduction
- Measuring trends in global consumption
- Global patterns and trends in the availability and consumption of water
- Global patterns and trends in the availability and consumption of land/food
- Global patterns and trends in the availability and consumption of energy
- Water food and energy nexus
- Recycling and waste
- Malthus vs Boserup
- Resource Stewardship strategies
- Sustainable Development Goals
-
Freshwater - drainage basins
>
- The drainage basin as a system
- How rivers change from source to mouth
- River discharge
- River processes
- River landforms
- Factors affecting flood risk
- Attempts at flood prediction
- Flood mitigation
- Flood mitigation case studies
- Water scarcity
- Agricultural activities and water quality
- Pressures on lakes and aquifers
- Internationally shared water and conflict
- Water management: participation of local communities
- Dams as multi-purpose schemes
- Water management: Integrated Drainage Basin Management (IDBM)
- Managing wetlands
-
Leisure, Sport and Tourism
>
- Growth and purpose of leisure time
- Categories of tourism and sport
- Economic development and participation
- Factors affecting personal participation
- Factors affecting growth of tourism hotspots
- Spheres of influencee
- Factors affecting a national sports league
- Festivals
- Niche national tourism strategies
- Role of TNCs
- Tourism as a national development strategy
- International sporting events
- Consequences of unsustainable growth
- Sustainable tourism
- Future international tourism
- Political and cultural influences on sport
- Extended Essay in Geography >
- Skills/concepts >
-
Changing population
>
- Geography and ToK
- Theory of Knowledge
Subject guide
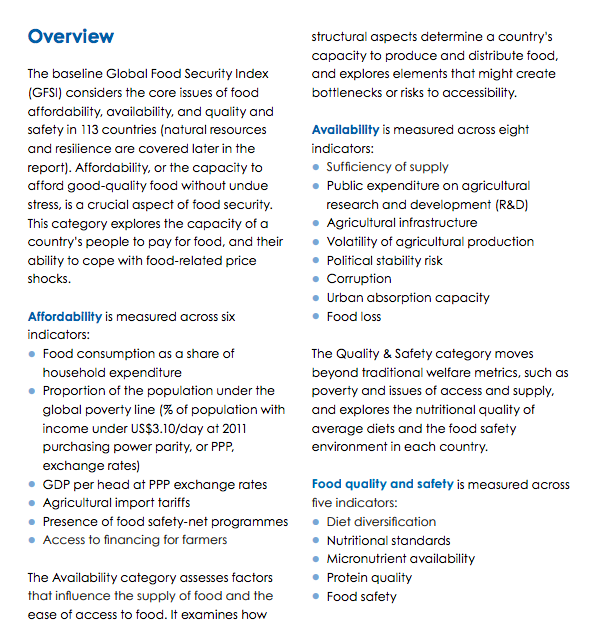
An overview of global patterns and trends in the availability and consumption of land/food, including changing diets in middle-income countries.
A. Land resources and productivity
Use the student textbook to answer the following questions:
- What has happened to the area of land used to grow crops as human population has increased?
- Use Fig 7.32 to briefly describe increases in the area of cropland worldwide.
- Now study Fig 7.33 and 7.34. What does this show us about changes between 1960 and 2000? Where has cropland expanded and where has it declined?
- Why is the area of cropland likely to increase or stay high in LICs? Why is it likely to decrease in HICs? Support this with examples. Where can you identify exceptions?
- Make sure you understand the index used to construct Fig 7.36. Wth reference to the graph, identify the regions with:
- The largest increases in food production
- The lowest rates of increase in food production between 1961 and 2013
- What is meant by farm productivity? Which parts of the world are experiencing the greatest and slowest increases in productivity.
- What factors are causing increasing productivity in most of the world?
B. Global patterns and trends in the availability of food
"Global food security has generally improved over the past decade, in line with record agricultural production and lower food prices. But recent macroeconomic, socio-economic and political trends suggest that continued progress is not a foregone conclusion. Fluctuating global economic growth, increasing inequality, political instability and forced migration, among many other factors, also have a significant impact on whether populations remain well-fed. Climate change and natural resource depletion will only aggravate these trends, while severely threatening the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (UN SDGs) of ending hunger by 2030. According to a recent study from the UN Food and Agricultural Organisation (FAO), by 2030 an extra 35m to 122m people could fall into poverty and therefore become less food secure as a result of climate-related risks."
Global Food Security Index 2017 p4
Global Food Security Index 2017 p4
|
Global Food Security Index
Use the resources in this section to answer the following questions:
|
| |||||||
Our World In Data: Hunger and Undernourishment
Study the map and graph below (source) and use the information to answer the following questions:
Study the map and graph below (source) and use the information to answer the following questions:
- Describe patterns of undernourishment in 2015.
- Comment on the situation in China, Niger, Indonesia, Singapore, USA.
- What is the overall trend?
- Why is there no data for HICs? Suggest reasons for the lack of data in other countries.
C. Changing Diets in MICs
- Based on the articles and TED Talk above and the student textbook, in what ways are the diets of the rising middle class changing?
- What is meant by "Food homogenisation"? Give evidence that it is occuring in the NGMC.
- Explain the impact of the changing diets of the rising middle class.
- How do the articles suggest that climate change is likely to compound these issues?
- Now form a pair. One of the pair should use the links and video below to investigate changing diet in Brazil and the other should focus on China. Prepare a mini case study for your country and then share it with your partner. It should include:
- Evidence of changing dietary trends and the nature of the change
- Causes of the changes - economic, demographic, social
- Consequences of the changes - economic, environmental, health, social
Brazil
China