-
MYP
- Home
-
IGCSE
- Course information
-
Physical: Hazardous environments
>
- Distribution of tectonic hazards
- Causes of tsunami
- Measuring earthquakes
- Earthquake case study 1: Haiti
- Earthquake case study 2: Christchurch
- Why do earthquakes do more damage in LICs than in HICs?
- How are volcanic eruptions measured?
- Tropical storms - distribution
- Causes of tropical cyclones
- Tropical cyclones - case study
- Why live in hazardous areas?
-
River Environments
>
- Hydrological cycle
- River basins
- Factors affecting river regimes
- Fluvial processes: erosion
- Fluvial processes: weathering and mass movement
- Fluvial processes: transportation and depositon
- River features and their formation
- How rivers change from source to mouth
- Uses of water
- Water pollution
- Water supply
-
IBDP
-
Changing population
>
- Global patterns of economic development
- Physical and human factors affecting global population distribution
- Case study 1: China
- Case study 2: Niger
- Demographic transition
- Megacity growth
- Forced migration and internal displacement
- Ageing populations
- Pro-natalist and anti-natalist policies
- Gender equality policies
- Trafficking policies
- The Demographic Dividend
-
Global climate vulnerability and resilience
>
- Atmospheric system
- The energy balance
- Changes in the energy balance
- The enhanced greenhouse effect
- Climate Change and the Hydrosphere, Atmosphere and Biosphere
- Impacts of climate change on people and places
- Disparities in exposure to climate change risk and vulnerability
- Government-led adaptation and mitigation strategies
- Civil society and corporate strategies
-
Global resource consumption and security
>
- Progress towards poverty reduction
- Measuring trends in global consumption
- Global patterns and trends in the availability and consumption of water
- Global patterns and trends in the availability and consumption of land/food
- Global patterns and trends in the availability and consumption of energy
- Water food and energy nexus
- Recycling and waste
- Malthus vs Boserup
- Resource Stewardship strategies
- Sustainable Development Goals
-
Freshwater - drainage basins
>
- The drainage basin as a system
- How rivers change from source to mouth
- River discharge
- River processes
- River landforms
- Factors affecting flood risk
- Attempts at flood prediction
- Flood mitigation
- Flood mitigation case studies
- Water scarcity
- Agricultural activities and water quality
- Pressures on lakes and aquifers
- Internationally shared water and conflict
- Water management: participation of local communities
- Dams as multi-purpose schemes
- Water management: Integrated Drainage Basin Management (IDBM)
- Managing wetlands
-
Leisure, Sport and Tourism
>
- Growth and purpose of leisure time
- Categories of tourism and sport
- Economic development and participation
- Factors affecting personal participation
- Factors affecting growth of tourism hotspots
- Spheres of influencee
- Factors affecting a national sports league
- Festivals
- Niche national tourism strategies
- Role of TNCs
- Tourism as a national development strategy
- International sporting events
- Consequences of unsustainable growth
- Sustainable tourism
- Future international tourism
- Political and cultural influences on sport
- Extended Essay in Geography >
- Skills/concepts >
-
Changing population
>
- Geography and ToK
- Theory of Knowledge
Study Guide
Factors affecting personal participation in sports and tourism, including affluence, gender, stage in lifecycle, personality, place of residence.
1. Affluence
We have already covered this in previous lessons - check the previous page to check on this.
2. Gender
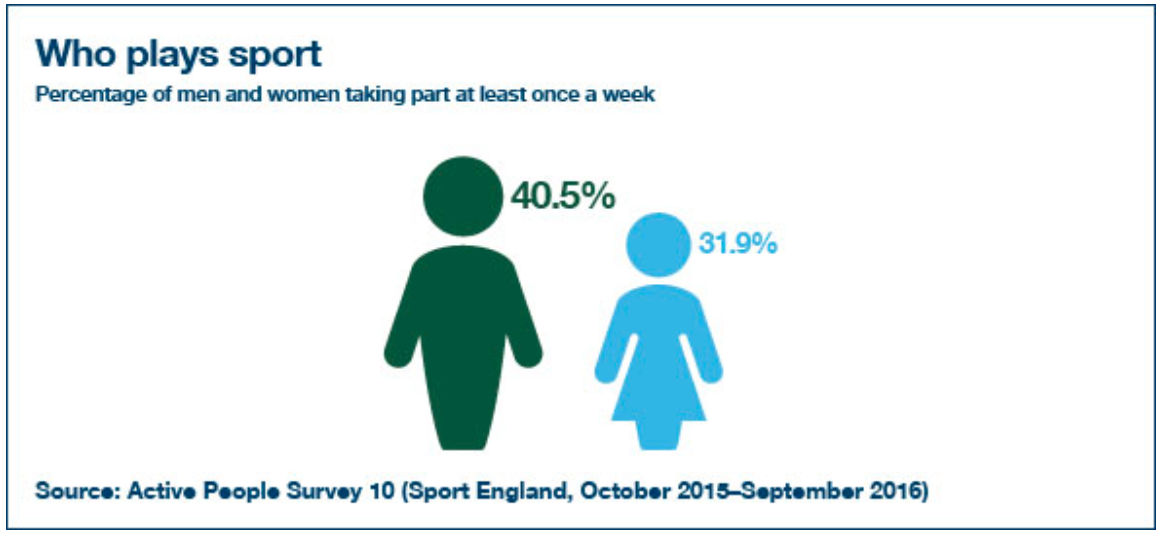
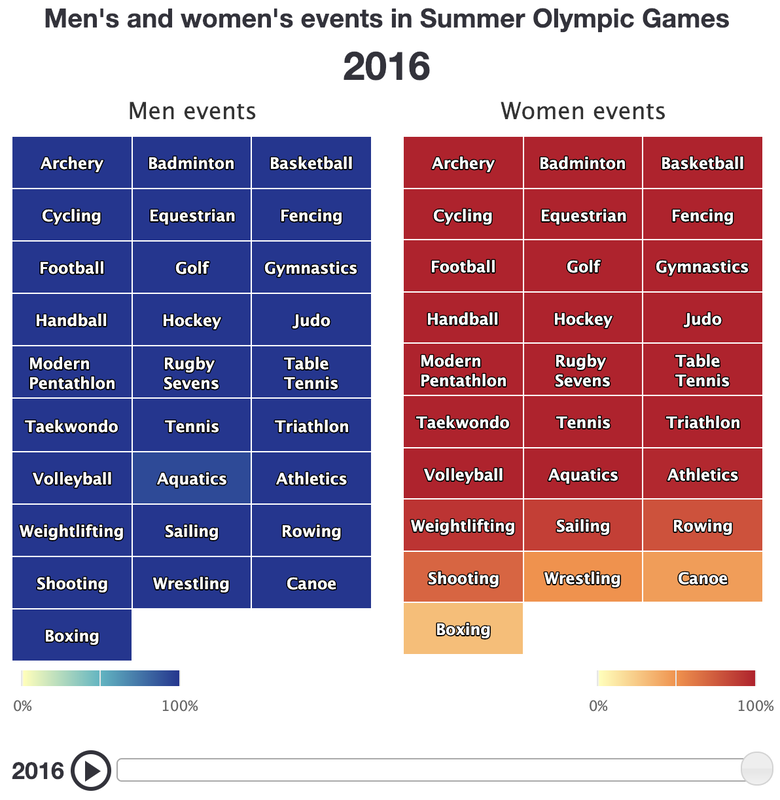
Gender is an influence in the decisions made by men and women in tourism, sport and leisure. The resources below focus on female participation in sport. Watch and explore the resources and then consider these questions:
- What is the difference between the number of adult men and women who participate in sport?
- How do each of the following factors contribute to this:
- Physiology
- Media portrayal of men and women in sport
- Family
- Societal pressure eg religion/tradition
Gender and tourism
What are the key points in the article below.
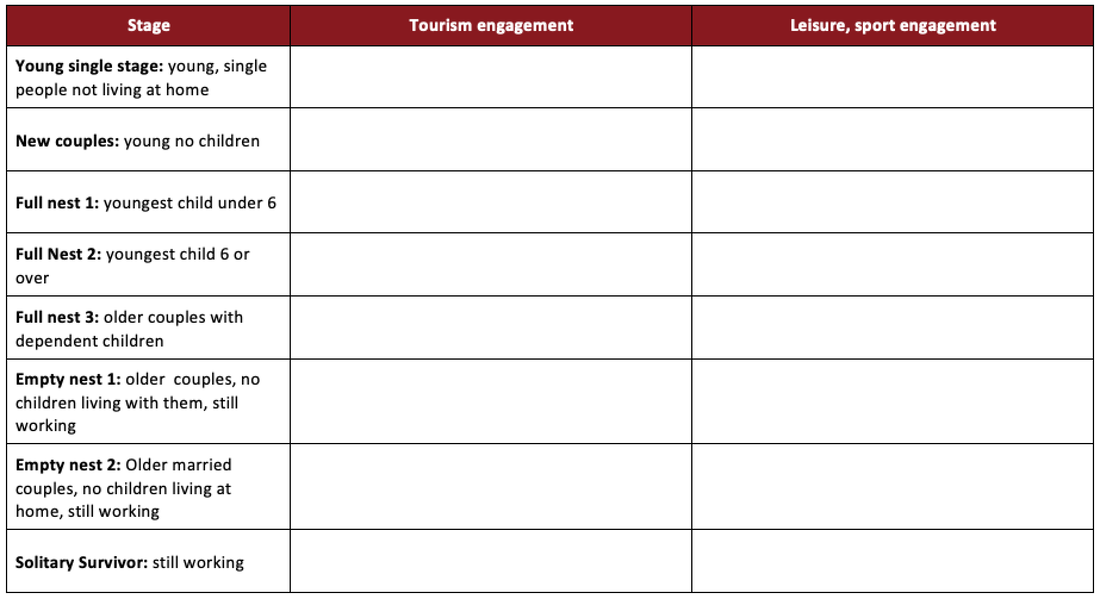
3. Life cycle stage
The decisions people make about leisure and tourism will be affected by their age and their family status. A single 30 year old woman with no children is likely to have different options than a woman of the same age with a partner and children for example; why is this the case? What factors will be different for the two women?
Study the table below which is one perspective on life cycles.
Study the table below which is one perspective on life cycles.
- Create your own copy of the table (or open the word doc linked from the image).
- Work in pairs to suggest what kind of tourism and leisure you think each group is likely to choose and why? As you do this consider the reasons why it is not a simple process.
- Which groups of people are missing from the table? How might their choices be different and why?
4. Personality
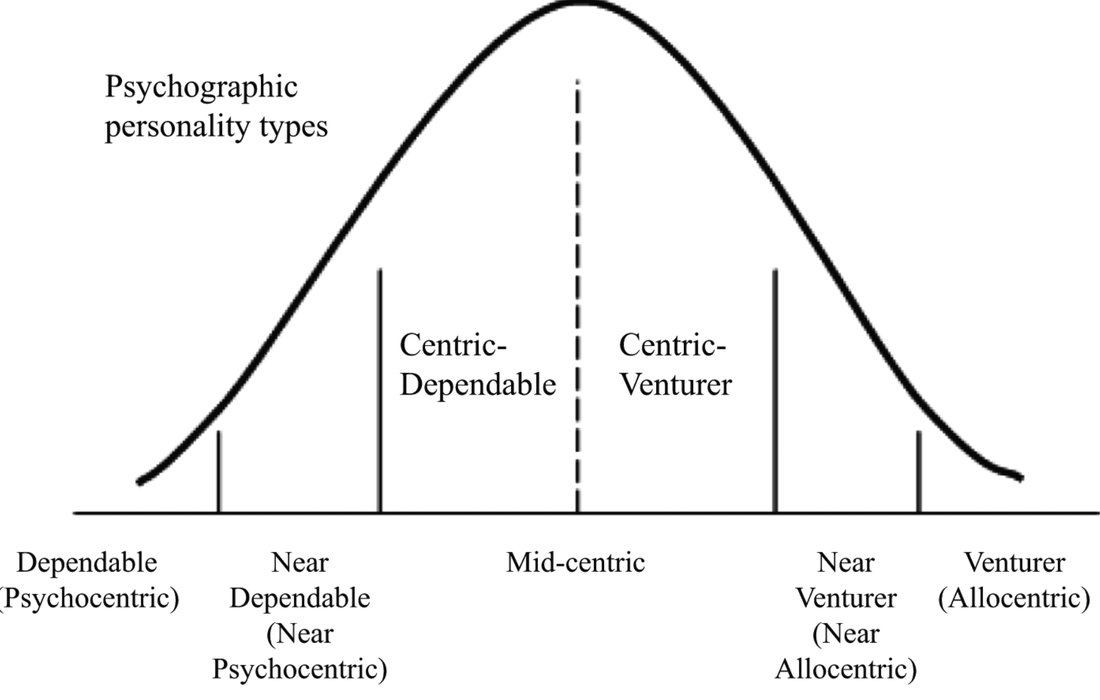
The decisions that people make about their personal participation in leisure and tourism will be strongly influenced by their personalities and preferences. Plog (1971) suggested that tourism choices were influenced by psychological factors.
Plog argues that tourist populations are like all other populations and can be characterised along a normal population distribution curve based on people's psychological profile. The profile is likely to affect:
Plog argues that tourist populations are like all other populations and can be characterised along a normal population distribution curve based on people's psychological profile. The profile is likely to affect:
- Desire to travel
- Frequency of travel
- Type of travel
- Destination Choice
- Type of activity
Allocentrics/venturers
A tourist who seeks new experiences and adventure in a wide range of activities. This person is outgoing and self-confident in behavior. An allocentric person prefers to fly and to explore new and unusual areas before others do so. Allocentrics enjoy meeting people from foreign or different cultures. They prefer good hotels and food, but not necessarily modern or chain-type hotels. For a tour package, an allocentric would like to have the basics such as transportation and hotels, but not be committed to a structured itinerary. They would rather have the freedom to explore an area, make their own arrangements and choose a variety of activities and tourist attractions.
Psychocentrics/dependables
A tourist falling in this category is usually non-adventuresome. They prefer to return to familiar travel destinations where they can relax and know what types of food and activity to expect. Such tourists prefer to drive to destinations, stay in typical accommodations, and eat at family-type restaurants.
A tourist who seeks new experiences and adventure in a wide range of activities. This person is outgoing and self-confident in behavior. An allocentric person prefers to fly and to explore new and unusual areas before others do so. Allocentrics enjoy meeting people from foreign or different cultures. They prefer good hotels and food, but not necessarily modern or chain-type hotels. For a tour package, an allocentric would like to have the basics such as transportation and hotels, but not be committed to a structured itinerary. They would rather have the freedom to explore an area, make their own arrangements and choose a variety of activities and tourist attractions.
Psychocentrics/dependables
A tourist falling in this category is usually non-adventuresome. They prefer to return to familiar travel destinations where they can relax and know what types of food and activity to expect. Such tourists prefer to drive to destinations, stay in typical accommodations, and eat at family-type restaurants.
- Study the images below
- For each image, briefly describe the type of holiday or leisure activity shown.
- Which personality type from Plog's theory do you think would be most likely to take part in this? Justify your answer?
- You should have found Q3 challenging; explain why you either needed more information or found it complicated. What does this tell us about the difficulty of classifying people's choices by personality.
5. Place of residence
There are many factors which are associated with place of residence which will affect people's participation in leisure, sport and tourism. These include:
- Availability of facilities eg golf or tennis courses
- Accessibility eg road links, airports, ports
- Political factors eg power of passports or government policy on sport and leisure developments
- Environmental factors eg weather, relief (consider skiing, mountain climbing, beach based leisure)
|
Explore the Passport Index website and consider the following questions:
|
|
Synposis... Read this BBC news story and consider the following questions:
|