-
MYP
- Home
-
IGCSE
- Course information
-
Physical: Hazardous environments
>
- Distribution of tectonic hazards
- Causes of tsunami
- Measuring earthquakes
- Earthquake case study 1: Haiti
- Earthquake case study 2: Christchurch
- Why do earthquakes do more damage in LICs than in HICs?
- How are volcanic eruptions measured?
- Tropical storms - distribution
- Causes of tropical cyclones
- Tropical cyclones - case study
- Why live in hazardous areas?
-
River Environments
>
- Hydrological cycle
- River basins
- Factors affecting river regimes
- Fluvial processes: erosion
- Fluvial processes: weathering and mass movement
- Fluvial processes: transportation and depositon
- River features and their formation
- How rivers change from source to mouth
- Uses of water
- Water pollution
- Water supply
-
IBDP
-
Changing population
>
- Global patterns of economic development
- Physical and human factors affecting global population distribution
- Case study 1: China
- Case study 2: Niger
- Demographic transition
- Megacity growth
- Forced migration and internal displacement
- Ageing populations
- Pro-natalist and anti-natalist policies
- Gender equality policies
- Trafficking policies
- The Demographic Dividend
-
Global climate vulnerability and resilience
>
- Atmospheric system
- The energy balance
- Changes in the energy balance
- The enhanced greenhouse effect
- Climate Change and the Hydrosphere, Atmosphere and Biosphere
- Impacts of climate change on people and places
- Disparities in exposure to climate change risk and vulnerability
- Government-led adaptation and mitigation strategies
- Civil society and corporate strategies
-
Global resource consumption and security
>
- Progress towards poverty reduction
- Measuring trends in global consumption
- Global patterns and trends in the availability and consumption of water
- Global patterns and trends in the availability and consumption of land/food
- Global patterns and trends in the availability and consumption of energy
- Water food and energy nexus
- Recycling and waste
- Malthus vs Boserup
- Resource Stewardship strategies
- Sustainable Development Goals
-
Freshwater - drainage basins
>
- The drainage basin as a system
- How rivers change from source to mouth
- River discharge
- River processes
- River landforms
- Factors affecting flood risk
- Attempts at flood prediction
- Flood mitigation
- Flood mitigation case studies
- Water scarcity
- Agricultural activities and water quality
- Pressures on lakes and aquifers
- Internationally shared water and conflict
- Water management: participation of local communities
- Dams as multi-purpose schemes
- Water management: Integrated Drainage Basin Management (IDBM)
- Managing wetlands
-
Leisure, Sport and Tourism
>
- Growth and purpose of leisure time
- Categories of tourism and sport
- Economic development and participation
- Factors affecting personal participation
- Factors affecting growth of tourism hotspots
- Spheres of influencee
- Factors affecting a national sports league
- Festivals
- Niche national tourism strategies
- Role of TNCs
- Tourism as a national development strategy
- International sporting events
- Consequences of unsustainable growth
- Sustainable tourism
- Future international tourism
- Political and cultural influences on sport
- Extended Essay in Geography >
- Skills/concepts >
-
Changing population
>
- Geography and ToK
- Theory of Knowledge
Study Guide
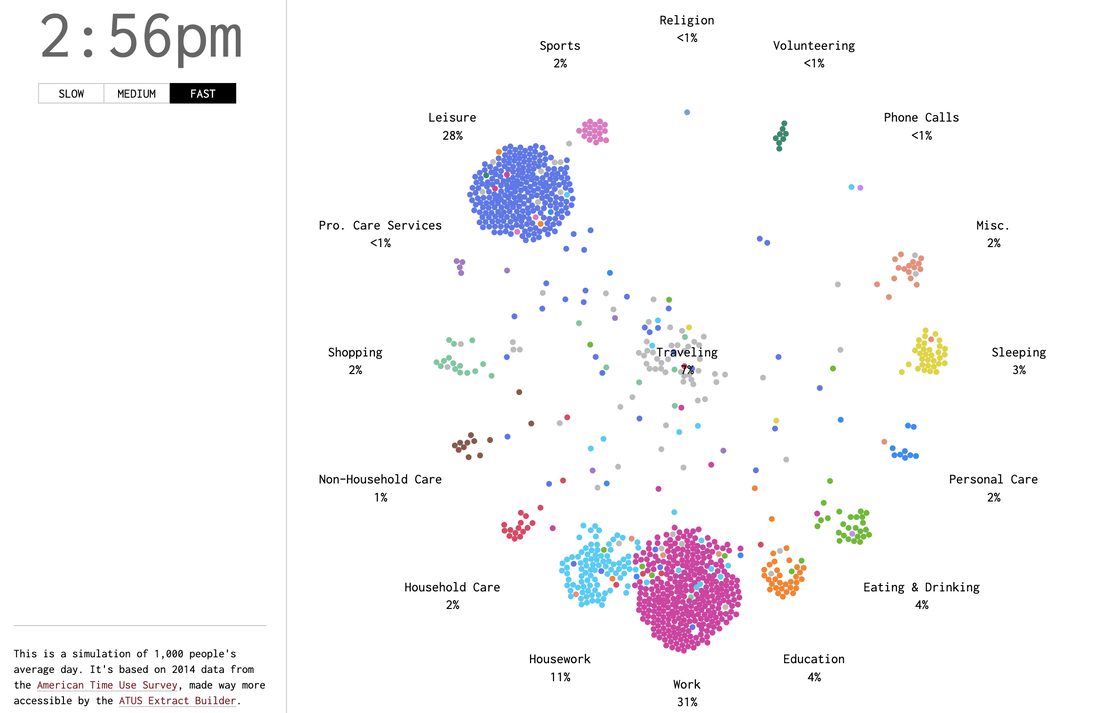
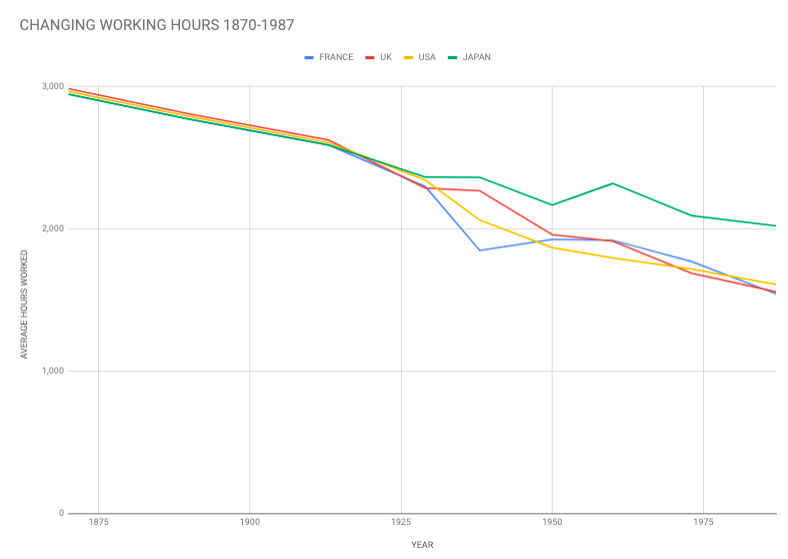
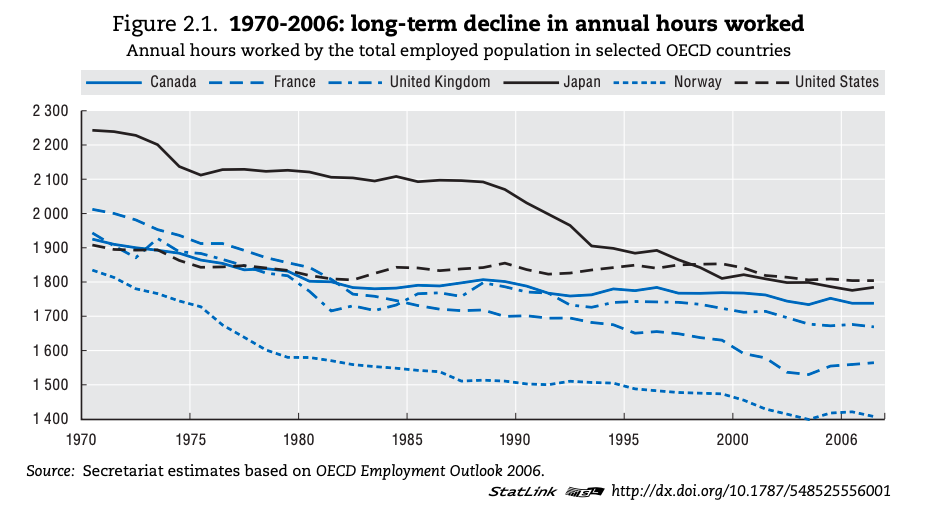
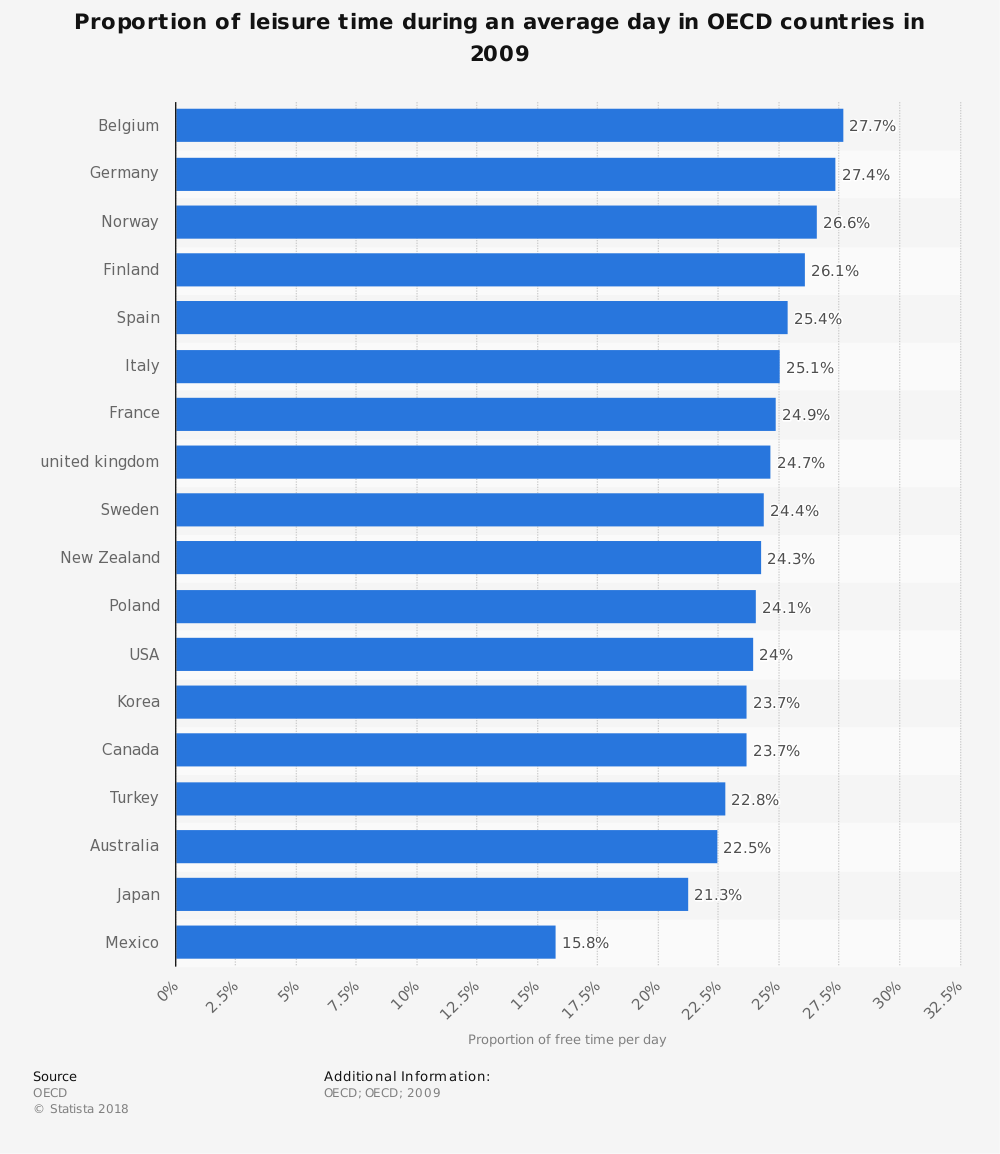
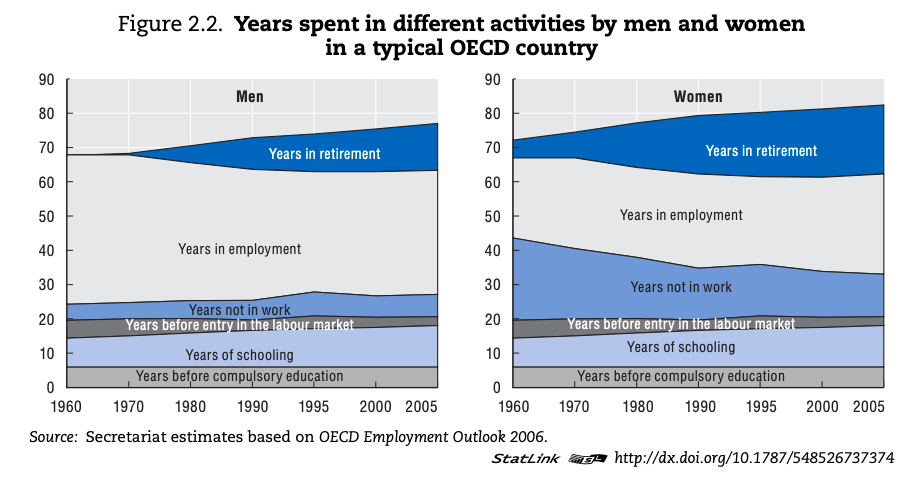
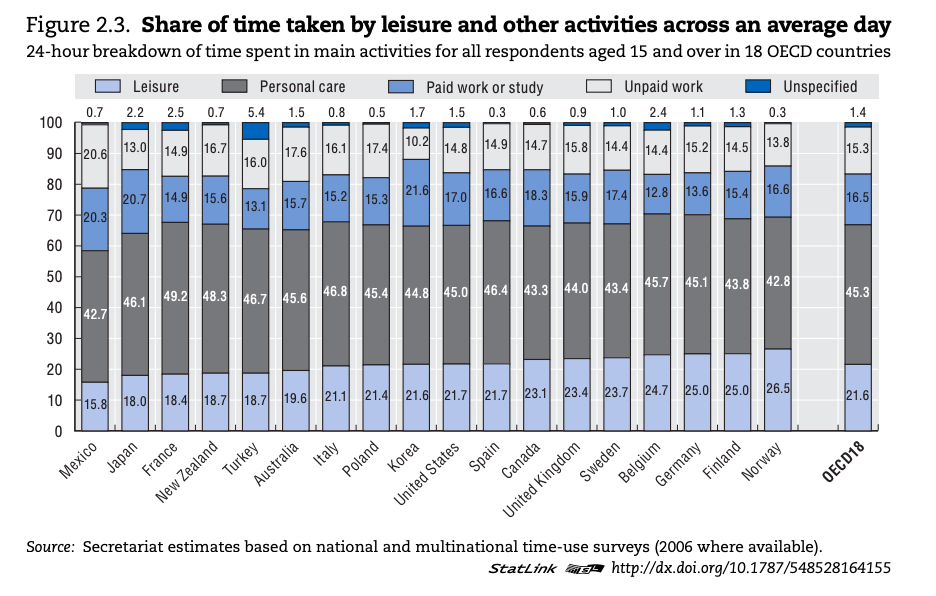
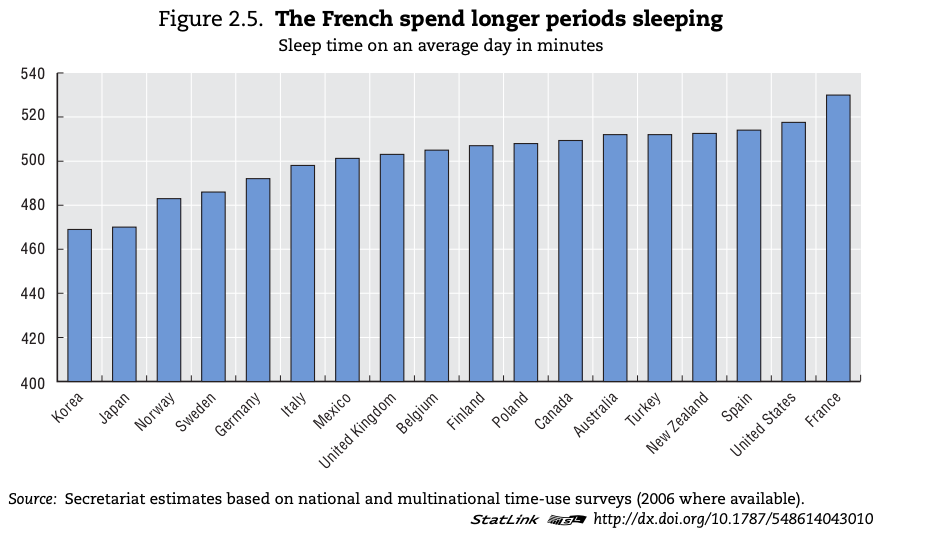
The growth and changing purpose of leisure time for societies in different geographic and developmental contexts.
Definitions
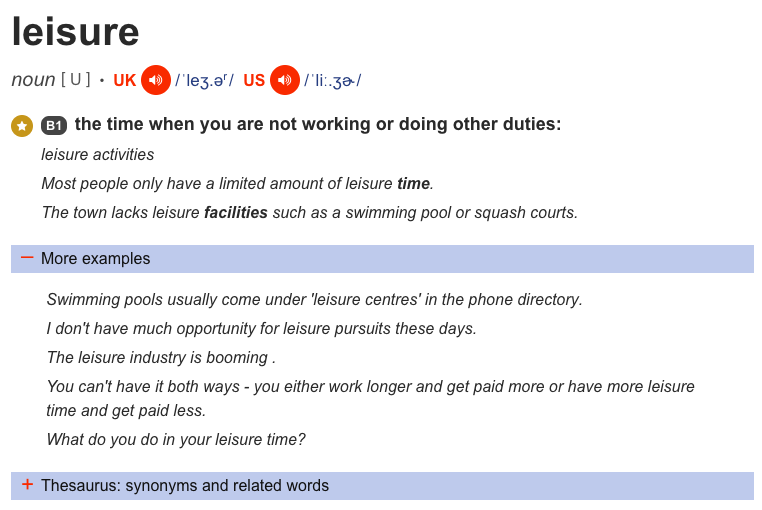
Leisure: Any freely chosen activity or experience that takes place in non-work time.
Sport: A physical activity involving a set of rules or customs. The activity may be competitive.
Tourism: Travel away from home for at least one night for the purpose of leisure (IB definition). I would argue that tourism does not have to involve a night away from home. I think people going on day trips should also be included in a definition of tourism.
Recreation: A leisure time activity undertaken voluntarily and for enjoyment.
Domestic tourism: Tourism within the country of residency.
International tourism: Tourism outside the country of residency.
Day trips (day tourism): Visits to places of interest e.g. the beach or a ruin, but without staying overnight.
Mass tourism or package holiday: Large-scale tourism when flights, accommodation, tours and transfers are booked together and often part of a group.
Sustainable tourism: Tourism that preserves primary tourist resources and supports the livelihoods and culture of local people.
Ecotourism: Like sustainable tourism, but with a focus on the natural environment.
Heritage tourism: Tourism based on historic legacy as its main focus e.g. natural landscape, historical buildings.
Honeypot: A location that attracts a large number of tourists. Antigua in Guatemala would be considered a honeypot location in Central America.
(Economic) Leakage: Money that is lost from a tourist destination. This money is often taken overseas by TNCs e.g. Intercontinental or Hilton.
Medical tourism: When people travel to other countries to undergo medical procedures e.g. dentistry or plastic surgery. This is done either because medical standards are better in the destination, or because medical treatment is cheaper in the destination.
Primary tourist/recreational resources: Pre-existing tourist attractions that often exist naturally e.g. the weather, wildlife, beaches, indigenous people or mountains.
Secondary tourist/recreational resources: Facilities that have been purposefully built for tourists e.g. hotels, restaurants, golf courses and airports.
Safari: Tourism that goes to view wildlife in its natural habitat. Safaris are very common in Africa e.g. Kenya, Tanzania and Botswana.
Resorts: A settlement where the primary function is tourism. Resorts are normally associated with the coast. Large hotel complexes are considered to be resorts.
Sports tours: Trips that either go to play sport or view sport. Trips to the football World Cup or Olympics are becoming much more common.
Health spas: Hotels or resorts that tourists visit for health treatments. This may include massages, detoxes or mud treatments.
All-inclusive: When tourists pay a hotel complex one price which includes all meals, drinks, entertainment, activities, etc. All-inclusive holidays are very common in the Mediterranean and the Caribbean.
Low-cost (budget) airlines: Airlines that offer cheaper than normal flights, by removing add ons like airport check-in, in flight meals, checked baggage and pre-selected seats.
Sport: A physical activity involving a set of rules or customs. The activity may be competitive.
Tourism: Travel away from home for at least one night for the purpose of leisure (IB definition). I would argue that tourism does not have to involve a night away from home. I think people going on day trips should also be included in a definition of tourism.
Recreation: A leisure time activity undertaken voluntarily and for enjoyment.
Domestic tourism: Tourism within the country of residency.
International tourism: Tourism outside the country of residency.
Day trips (day tourism): Visits to places of interest e.g. the beach or a ruin, but without staying overnight.
Mass tourism or package holiday: Large-scale tourism when flights, accommodation, tours and transfers are booked together and often part of a group.
Sustainable tourism: Tourism that preserves primary tourist resources and supports the livelihoods and culture of local people.
Ecotourism: Like sustainable tourism, but with a focus on the natural environment.
Heritage tourism: Tourism based on historic legacy as its main focus e.g. natural landscape, historical buildings.
Honeypot: A location that attracts a large number of tourists. Antigua in Guatemala would be considered a honeypot location in Central America.
(Economic) Leakage: Money that is lost from a tourist destination. This money is often taken overseas by TNCs e.g. Intercontinental or Hilton.
Medical tourism: When people travel to other countries to undergo medical procedures e.g. dentistry or plastic surgery. This is done either because medical standards are better in the destination, or because medical treatment is cheaper in the destination.
Primary tourist/recreational resources: Pre-existing tourist attractions that often exist naturally e.g. the weather, wildlife, beaches, indigenous people or mountains.
Secondary tourist/recreational resources: Facilities that have been purposefully built for tourists e.g. hotels, restaurants, golf courses and airports.
Safari: Tourism that goes to view wildlife in its natural habitat. Safaris are very common in Africa e.g. Kenya, Tanzania and Botswana.
Resorts: A settlement where the primary function is tourism. Resorts are normally associated with the coast. Large hotel complexes are considered to be resorts.
Sports tours: Trips that either go to play sport or view sport. Trips to the football World Cup or Olympics are becoming much more common.
Health spas: Hotels or resorts that tourists visit for health treatments. This may include massages, detoxes or mud treatments.
All-inclusive: When tourists pay a hotel complex one price which includes all meals, drinks, entertainment, activities, etc. All-inclusive holidays are very common in the Mediterranean and the Caribbean.
Low-cost (budget) airlines: Airlines that offer cheaper than normal flights, by removing add ons like airport check-in, in flight meals, checked baggage and pre-selected seats.
Leisure time - what is leisure?
Leisure time
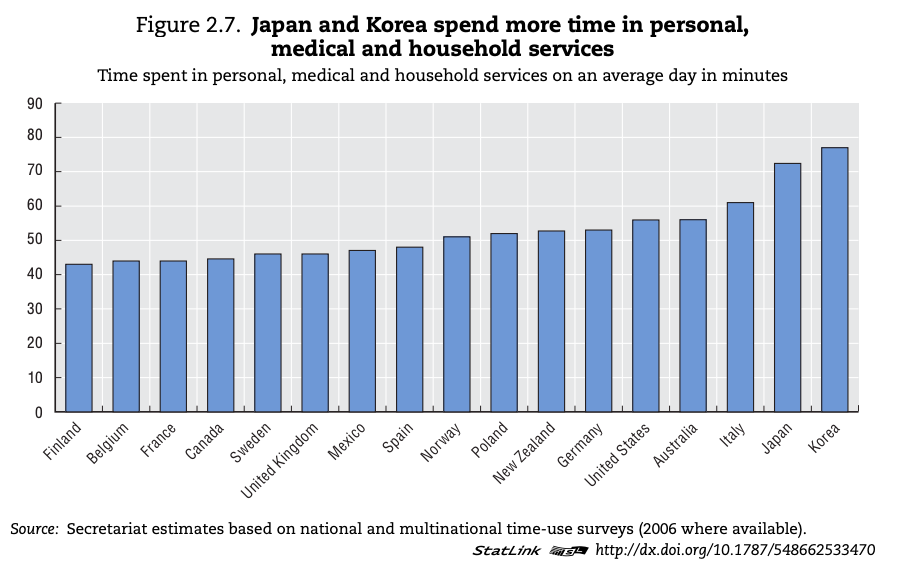
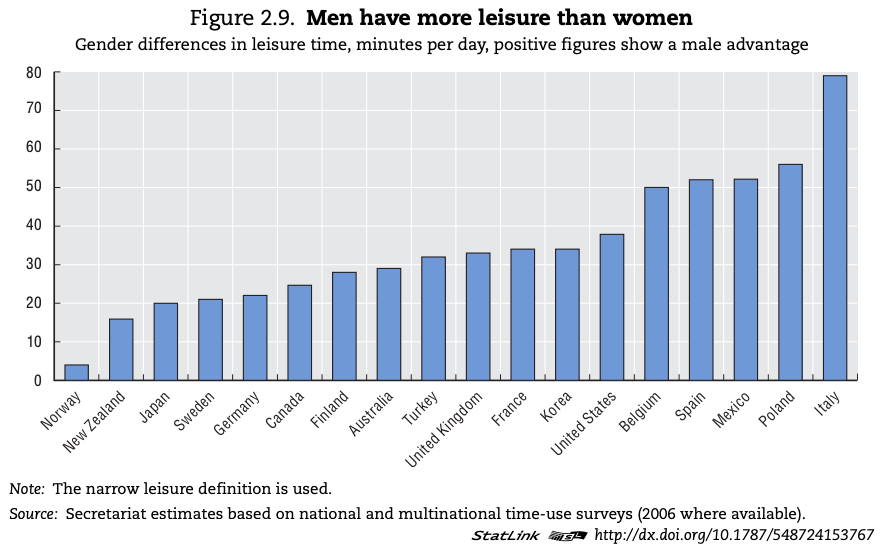
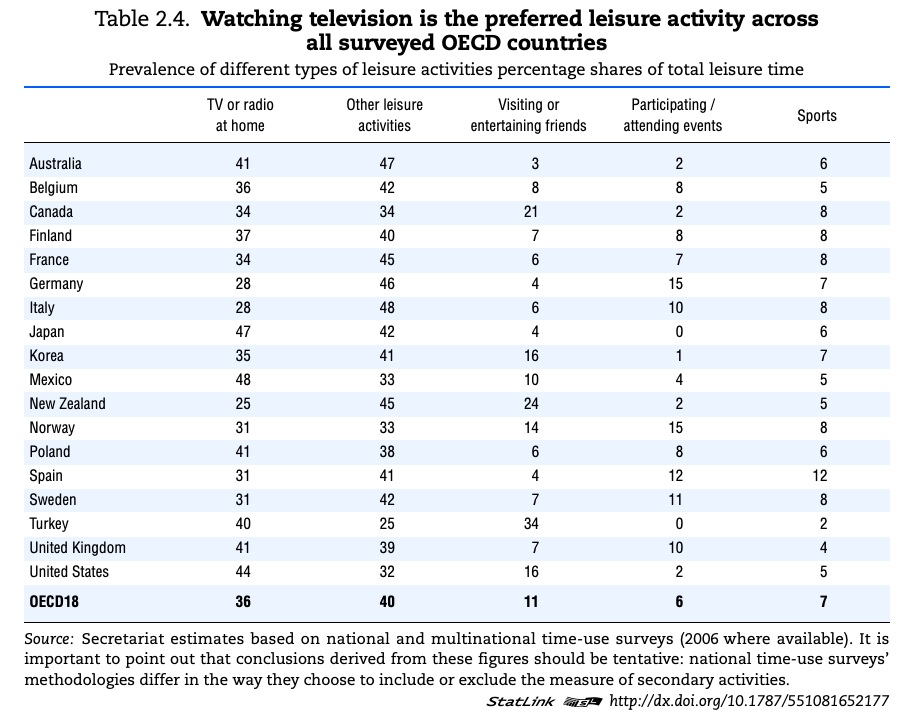
Study the sources below