Trade and development
What is trade?
When we talk about trade in Geography we are referring to any transaction or exchange of goods and services. This might be one country trading with another country, eg Kenya selling fruit and flowers to the UK; it might be trade between villages or even between individuals.
Trade is usually good for the country which is selling goods and products as it is a way to make money which can be used to build the infrastructure and services within the country through the payment of taxes.
This section on trade will focus mostly on international trade between countries.
Trade is usually good for the country which is selling goods and products as it is a way to make money which can be used to build the infrastructure and services within the country through the payment of taxes.
This section on trade will focus mostly on international trade between countries.
Imports
These are goods or products that a country buys from another country. For example, Indonesia importing manufactured toys from China.
Exports
These are goods or products that a country sells to another country. For example, Indonesia exports textiles to China.
Is trade always good for development?
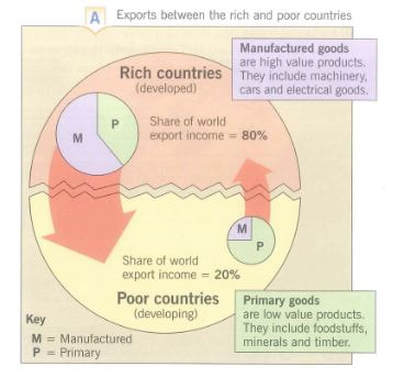
Trade is usually good for development but sometimes it can be damaging because of unfair conditions and prices or because of the value of the products being traded. Most of profits from global trade go to businesses and people in economically more developed countries. See the diagram below from "Interactions" by David Waugh.
|
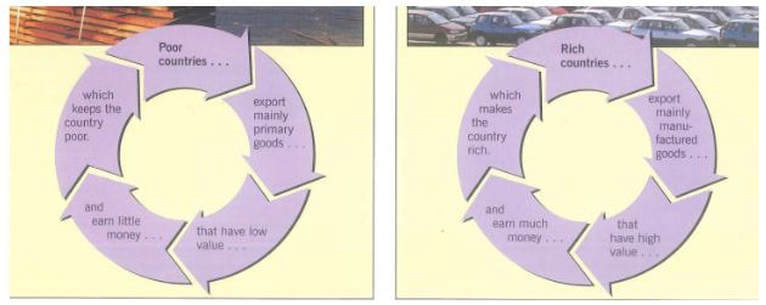
Now look at the two cycles below which show how sometimes trade can keep the poorest countries poor and keep the richer countries rich.
Describe what they show in your own words. How do these diagrams suggest that trade keeps the rich countries rich and the poor countries poor?
Describe what they show in your own words. How do these diagrams suggest that trade keeps the rich countries rich and the poor countries poor?
It can also be a problem if a country depends too much on a single product or commodity. Look at the diagram below (also from Waugh's Interactions) to see some examples.
The videos below give some other viewpoints on global trade. Watch them and see if you agree?
|
|
|
The Trade Game
Once your class have played the trading game, consider the questions below:
- During the trade game we had to……
- The rules of the game were……
- The richer countries were given…
- The middle countries were given…
- The least wealthy countries were given……
- What did the sheets of paper represent?
- What did the scissors, rulers, pencils, compasses etc represent?
- What problems did the LEDCs have in trying to develop through trade?
- What problem did the MEDCs have? How did they solve it?
- What did the big companies(TNCs) offer some of the countries in the game? How real do you think this is?
- What do you think the stickers represented? What happened with these and who knew about it? Can you think of any examples when this might happen in the real world?
- Richer countries can trade easily because…(what do they trade? How does this keep them rich? You could include a diagram).
- Poorer countries find it hard to trade because…(what do they tend to trade in? Why does this keep them poor? What is meant by “dependency” and how can this affect a country’s ability to develop)
- Try to explain why world trade won’t usually help the poorest countries to develop.
- I think that trade is fair/not fair because….
- To make trade better countries could….
| trading_game_instructions.pdf |
Trade assessment
Trade can help countries to achieve economic development but it can also keep poor countries poor while making rich countries richer. Discuss this statement including reference to both the trade game and real world examples of the effects of trade.
Possible structure:
- Introduction: what is trade? Why is trade important to help countries develop?
- The trade game and what it showed about trade - what were the advantages of the rich countries and the problems faced by the poorer countries? How does this reflect the real world?
- Problems of trade 1- vicious/virtuous circles of trade for richer/poorer countries (see above). How can trade sometimes work for the richer countries and not for LICs? Give examples from your own research. Can you connect this to the trade game as well?
- Problems of trade 2 - dependence on a single product. Why is it risky for a country to depend on a single product or resource (see above). Give examples. Can you also connect this to the trade game?
- Possible solutions - you could look at campaigns like Fair Trade. What would you suggest? Was there any way that the LICs in the trade game could have worked together to do better?
- Conclusion - what are the advantages and disadvantages of trade for LICs? On balance is it positive or negative in your opinion? Justify what you say.