-
MYP
- Home
-
IGCSE
- Course information
-
Physical: Hazardous environments
>
- Distribution of tectonic hazards
- Causes of tsunami
- Measuring earthquakes
- Earthquake case study 1: Haiti
- Earthquake case study 2: Christchurch
- Why do earthquakes do more damage in LICs than in HICs?
- How are volcanic eruptions measured?
- Tropical storms - distribution
- Causes of tropical cyclones
- Tropical cyclones - case study
- Why live in hazardous areas?
-
River Environments
>
- Hydrological cycle
- River basins
- Factors affecting river regimes
- Fluvial processes: erosion
- Fluvial processes: weathering and mass movement
- Fluvial processes: transportation and depositon
- River features and their formation
- How rivers change from source to mouth
- Uses of water
- Water pollution
- Water supply
-
IBDP
-
Changing population
>
- Global patterns of economic development
- Physical and human factors affecting global population distribution
- Case study 1: China
- Case study 2: Niger
- Demographic transition
- Megacity growth
- Forced migration and internal displacement
- Ageing populations
- Pro-natalist and anti-natalist policies
- Gender equality policies
- Trafficking policies
- The Demographic Dividend
-
Global climate vulnerability and resilience
>
- Atmospheric system
- The energy balance
- Changes in the energy balance
- The enhanced greenhouse effect
- Climate Change and the Hydrosphere, Atmosphere and Biosphere
- Impacts of climate change on people and places
- Disparities in exposure to climate change risk and vulnerability
- Government-led adaptation and mitigation strategies
- Civil society and corporate strategies
-
Global resource consumption and security
>
- Progress towards poverty reduction
- Measuring trends in global consumption
- Global patterns and trends in the availability and consumption of water
- Global patterns and trends in the availability and consumption of land/food
- Global patterns and trends in the availability and consumption of energy
- Water food and energy nexus
- Recycling and waste
- Malthus vs Boserup
- Resource Stewardship strategies
- Sustainable Development Goals
-
Freshwater - drainage basins
>
- The drainage basin as a system
- How rivers change from source to mouth
- River discharge
- River processes
- River landforms
- Factors affecting flood risk
- Attempts at flood prediction
- Flood mitigation
- Flood mitigation case studies
- Water scarcity
- Agricultural activities and water quality
- Pressures on lakes and aquifers
- Internationally shared water and conflict
- Water management: participation of local communities
- Dams as multi-purpose schemes
- Water management: Integrated Drainage Basin Management (IDBM)
- Managing wetlands
-
Leisure, Sport and Tourism
>
- Growth and purpose of leisure time
- Categories of tourism and sport
- Economic development and participation
- Factors affecting personal participation
- Factors affecting growth of tourism hotspots
- Spheres of influencee
- Factors affecting a national sports league
- Festivals
- Niche national tourism strategies
- Role of TNCs
- Tourism as a national development strategy
- International sporting events
- Consequences of unsustainable growth
- Sustainable tourism
- Future international tourism
- Political and cultural influences on sport
- Extended Essay in Geography >
- Skills/concepts >
-
Changing population
>
- Geography and ToK
- Theory of Knowledge
|
|
|
Fair Trade TV -your group challenge
As a team you need to plan and script a TV report on Fair Trade.
Each of you will need to carry out two main tasks:
Each of you will need to carry out two main tasks:
- Work with the rest of your group to read the material you have been given and to plan what the report should include.
- Take a role in the report itself.
What does the news story need to include?
- What are the problems with “traditional trade”? Why does it not help people to improve their lives?
- What is fair trade? How is it different from regular trade? What is good about it? How has it grown? Why?
- How has fair trade improved people’s lives? Examples?
- What are the limitations of Fair Trade?
Possible roles
- Studio anchorperson (the main newsreader) – this person will have to hold the whole piece together and will need to work with all of the others to plan the order and script for the piece
- Expert on World Trade (who can explain what the problem is with World Trade) – this person will need to learn all they can about the problems with trade for people in LEDCs. They then need to work with the anchor person to decide on their script/interview. You will also need to know about the limitations of fair trade.
- Representative of the Fair Trade Federation to explain what is meant by Fair Trade and how it works. This person will need to learn all that they can about what Fair Trade means and need to be able to explain how it works, what it aims to do and how it can improve the lives of people in LEDCs then plan your script/interview with the anchorperson.
- Farmer who has been affected by Fair Trade who can explain how it has improved their lives. This person will need to be able to explain what their lives were like before and after they became involved in Fair Trade. You will need to be able to describe your life but it’s also really important that you work to come across as a real person who people will relate to.
- Reporter on location to interview the farmer. This person will set the scene before the interview with the farmer by explaining where they are, what is being grown and what changes Fairtrade has brought to the area. You’ll need to use the information about the farmer and also will need to know how Fair Trade affects lives.
A. How does Fair Trade work and how does it help?
|
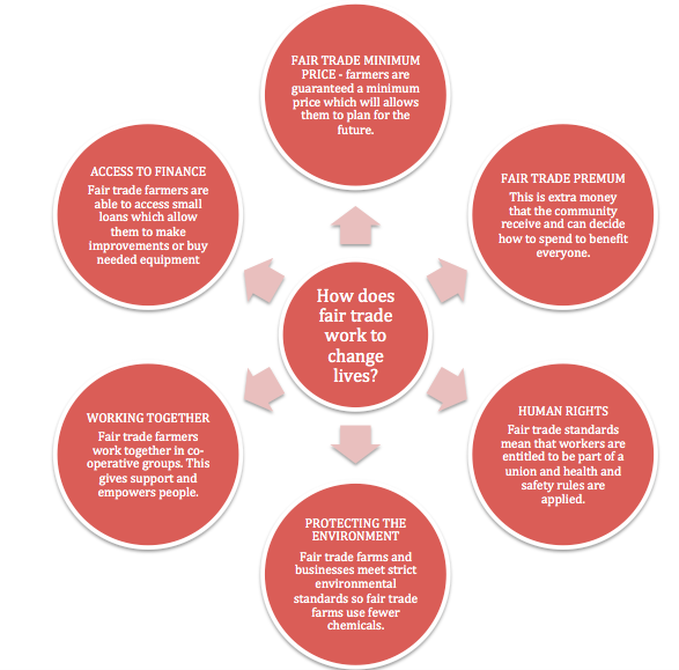
Fair trade aims to work differently from traditional trade by putting people and the environment at the centre of what they do. Key aspects of how Fair Trade works to improve life for workers, build communities and protect the environment are shown in the diagram on the left. Watch the videos and check the links below to add more detail/depth to your understanding. |
|
This list gives a good summary of some of the benefits of being involved in fair trade for people and communities in LEDCs. How is it different from what you already know about traditional trade? Check this page if you need to remind yourself: Trade and development |
|
|
|
B. What are the problems with traditional trade?
Remember to refer to what you have already learned about the costs and benefits of traditional trade! Check here: Trade and development
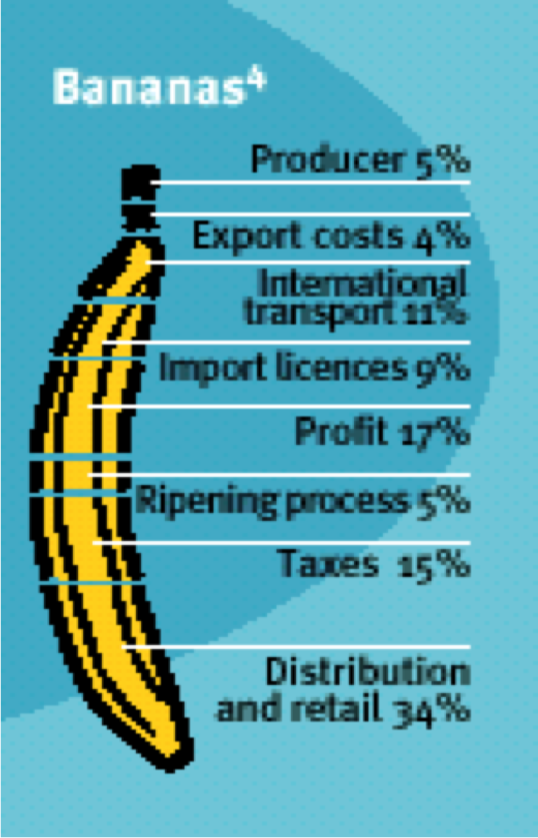
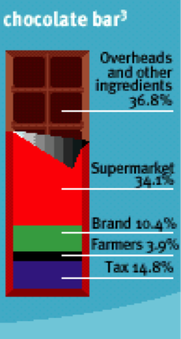
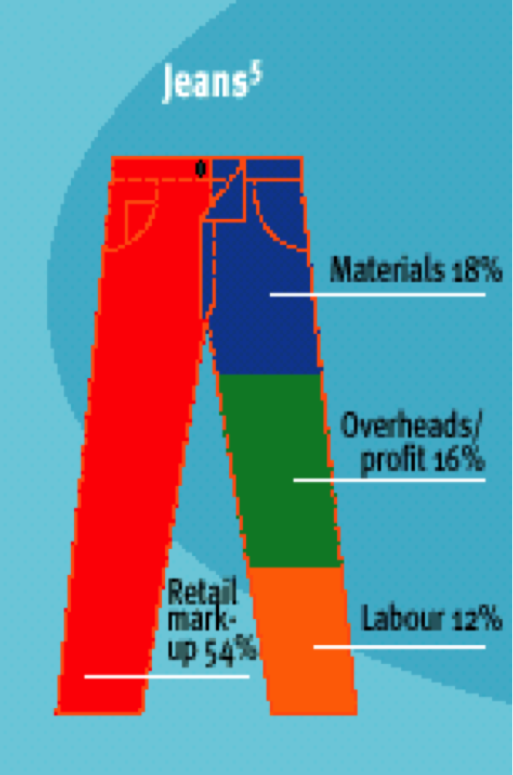
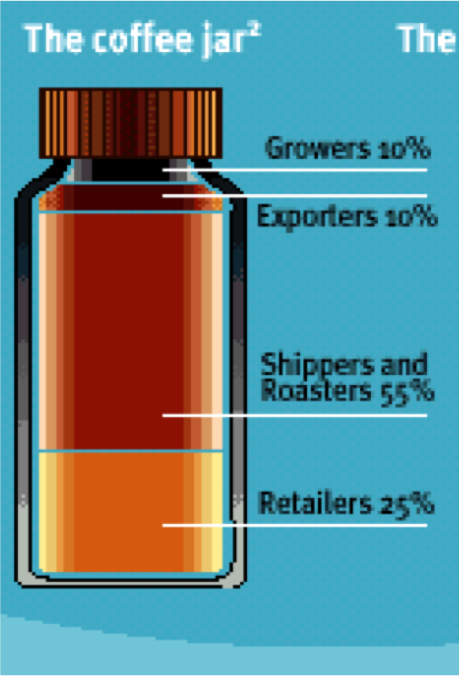
The four graphics below show who benefits from profits from bananas, chocolate, jeans and instant coffee under traditional trade. Look carefully at how much the producers/farmers/workers/growers receive compared to "big business". What ethical questions does this raise and why?
The four graphics below show who benefits from profits from bananas, chocolate, jeans and instant coffee under traditional trade. Look carefully at how much the producers/farmers/workers/growers receive compared to "big business". What ethical questions does this raise and why?
|
|
|
C. How Fair Trade has changed lives of people in LEDCS/LICs
Use the file below to find the stories of:
- Fyson Tchale (tea farmer in Malawi)
- Ruberra Figueraa (sugar cane farmer in Belize)
- Fortin Bleu (Cocoa Farmer in Côte d'Ivoire)
| fair_trade_action_guide_with_farmer_stories.pdf | |
| File Size: | 5537 kb |
| File Type: | |
More true stories from farmers around the world whose lives have been affected by Fair Trade. Each pdf file is a different farmer:
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||
What are the limitations and criticisms of fair trade?
|
|
|