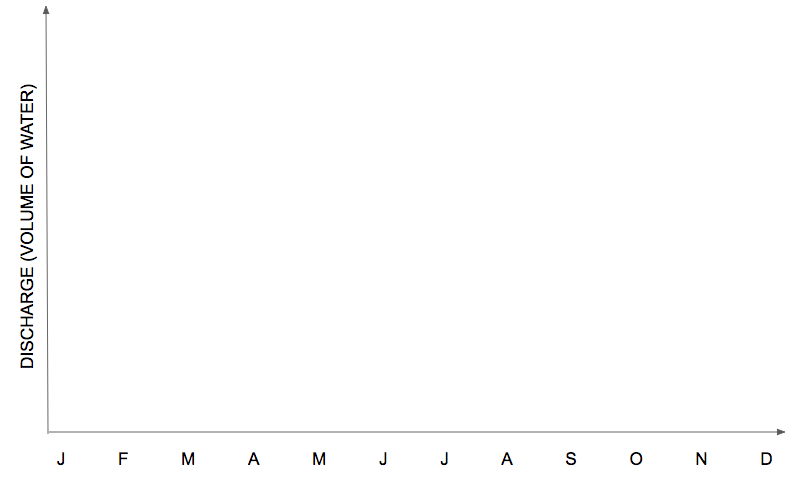-
MYP
- Home
-
IGCSE
- Course information
-
Physical: Hazardous environments
>
- Distribution of tectonic hazards
- Causes of tsunami
- Measuring earthquakes
- Earthquake case study 1: Haiti
- Earthquake case study 2: Christchurch
- Why do earthquakes do more damage in LICs than in HICs?
- How are volcanic eruptions measured?
- Tropical storms - distribution
- Causes of tropical cyclones
- Tropical cyclones - case study
- Why live in hazardous areas?
-
River Environments
>
- Hydrological cycle
- River basins
- Factors affecting river regimes
- Fluvial processes: erosion
- Fluvial processes: weathering and mass movement
- Fluvial processes: transportation and depositon
- River features and their formation
- How rivers change from source to mouth
- Uses of water
- Water pollution
- Water supply
-
IBDP
-
Changing population
>
- Global patterns of economic development
- Physical and human factors affecting global population distribution
- Case study 1: China
- Case study 2: Niger
- Demographic transition
- Megacity growth
- Forced migration and internal displacement
- Ageing populations
- Pro-natalist and anti-natalist policies
- Gender equality policies
- Trafficking policies
- The Demographic Dividend
-
Global climate vulnerability and resilience
>
- Atmospheric system
- The energy balance
- Changes in the energy balance
- The enhanced greenhouse effect
- Climate Change and the Hydrosphere, Atmosphere and Biosphere
- Impacts of climate change on people and places
- Disparities in exposure to climate change risk and vulnerability
- Government-led adaptation and mitigation strategies
- Civil society and corporate strategies
-
Global resource consumption and security
>
- Progress towards poverty reduction
- Measuring trends in global consumption
- Global patterns and trends in the availability and consumption of water
- Global patterns and trends in the availability and consumption of land/food
- Global patterns and trends in the availability and consumption of energy
- Water food and energy nexus
- Recycling and waste
- Malthus vs Boserup
- Resource Stewardship strategies
- Sustainable Development Goals
-
Freshwater - drainage basins
>
- The drainage basin as a system
- How rivers change from source to mouth
- River discharge
- River processes
- River landforms
- Factors affecting flood risk
- Attempts at flood prediction
- Flood mitigation
- Flood mitigation case studies
- Water scarcity
- Agricultural activities and water quality
- Pressures on lakes and aquifers
- Internationally shared water and conflict
- Water management: participation of local communities
- Dams as multi-purpose schemes
- Water management: Integrated Drainage Basin Management (IDBM)
- Managing wetlands
-
Leisure, Sport and Tourism
>
- Growth and purpose of leisure time
- Categories of tourism and sport
- Economic development and participation
- Factors affecting personal participation
- Factors affecting growth of tourism hotspots
- Spheres of influencee
- Factors affecting a national sports league
- Festivals
- Niche national tourism strategies
- Role of TNCs
- Tourism as a national development strategy
- International sporting events
- Consequences of unsustainable growth
- Sustainable tourism
- Future international tourism
- Political and cultural influences on sport
- Extended Essay in Geography >
- Skills/concepts >
-
Changing population
>
- Geography and ToK
- Theory of Knowledge
Specification
Factors affecting river regimes: precipitation including storm hydrographs, temperature, vegetation, land-use, water abstraction, dams.
What is a "river regime"?
The regime of a river is the way in which the discharge of the river changes over time or in the course of the year.
How would the regime of a river be affected by each of the following:
Sketch a set of axes like the ones shown below on a mini-whiteboard and work in pairs to draw and try to explain how you think the river regime would look for each of the rivers listed:
How would the regime of a river be affected by each of the following:
- A sudden intense period of rainfall
- Snow melting on mountains at the end of summer
- A long period of drought
Sketch a set of axes like the ones shown below on a mini-whiteboard and work in pairs to draw and try to explain how you think the river regime would look for each of the rivers listed:
- A river on Java, Indonesia
- A river in northern Nigeria, on the edge of the Sahel. Rain falls only between June and August
- A river in NW Europe where precipitation falls year round. During the winter months precipitation falls as snow which does not melt until March.
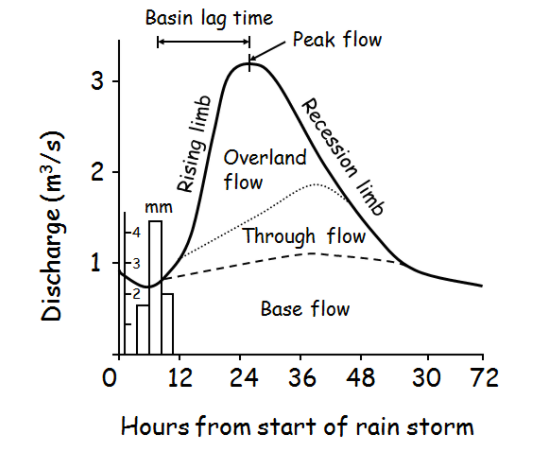
Storm hydrographs (also known as Flood Hydrographs)
|
A storm hydrograph is a special kind of graph which shows how the discharge of a stream or river changes after a period of rainfall.
You need to :
|
a) Key features of a hydrograph
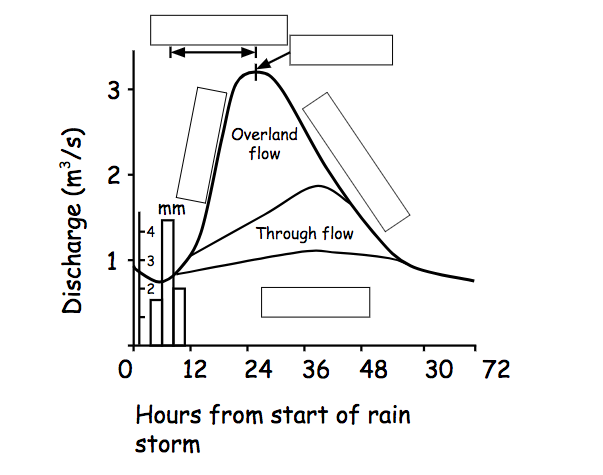
b) Drawing a hydrograph
Use the data you have been given to practise drawing your own storm hydrograph. Check that you have included/done all of the following:
- Graph has a clear title
- All axes are clearly labelled
- Each of the following are labelled:
- Peak flow (label includes the time and the discharge)
- Peak rainfall (label includes time and amount of rainfall)
- Lag time (this is shown diagramatically and has been calculated)
- Rising limb
- Recession limb
c) Hydrographs in action
Watch the video clip below carefully. Can you write a commentary which explains and links what you see to the storm hydrograph?!
|
|
Now work in 2s or 3s and discuss what effect each of the following would have on the lag time and the peak discharge:
|